# 选择排序
时间复杂度:O(N^2)
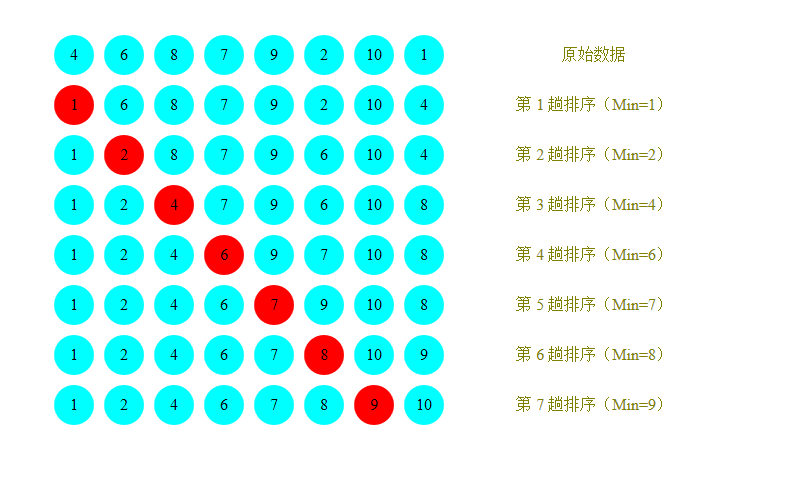
- 每一次遍历的过程中,都假定第一个索引处的元素是最小值,和其他索引处的值依次进行比较,如果当前索引处的值大于其他某个索引处的值,则假定其他某个索引出的值为最小值,最后可以找到最小值所在的索引
- 交换第一个索引处和最小值所在的索引处的值
# 需求
给定一段数组,将他排序由小到大
如:排序前:{4,5,6,3,2,1},排序后:{1,2,3,4,5,6}
# 实现
public class Selection {
/**
* 对数组a中的元素进行排序
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a){
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 2; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) {
if (greater(a[minIndex], a[j])) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
exch(a, i, minIndex);
}
}
/**
* 比较v元素是否大于w元素
*/
private static boolean greater(Comparable v,Comparable w){
return v.compareTo(w) > 0;
}
/**
* 数组元素i和j交换位置
*/
private static void exch(Comparable[] a,int i,int j){
Comparable temp;
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
测试
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] a = {4, 5, 6, 3, 2, 1};
Selection.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//123456
}
}